Content pruning refers to the methodical removal of outdated, irrelevant, or underperforming web pages.
Think of it as trimming dead branches off a tree. The goal is to encourage stronger, more focused growth — in this case, better SEO performance.
By cutting away what no longer serves your strategy, your site can become leaner, faster, and more attractive to search engines.
How to Prune Your Website Content
You don’t need to do this daily, but running a content pruning session once or twice a year can help you stay ahead.
Here’s how the process works:
Step 1: Audit Your Content
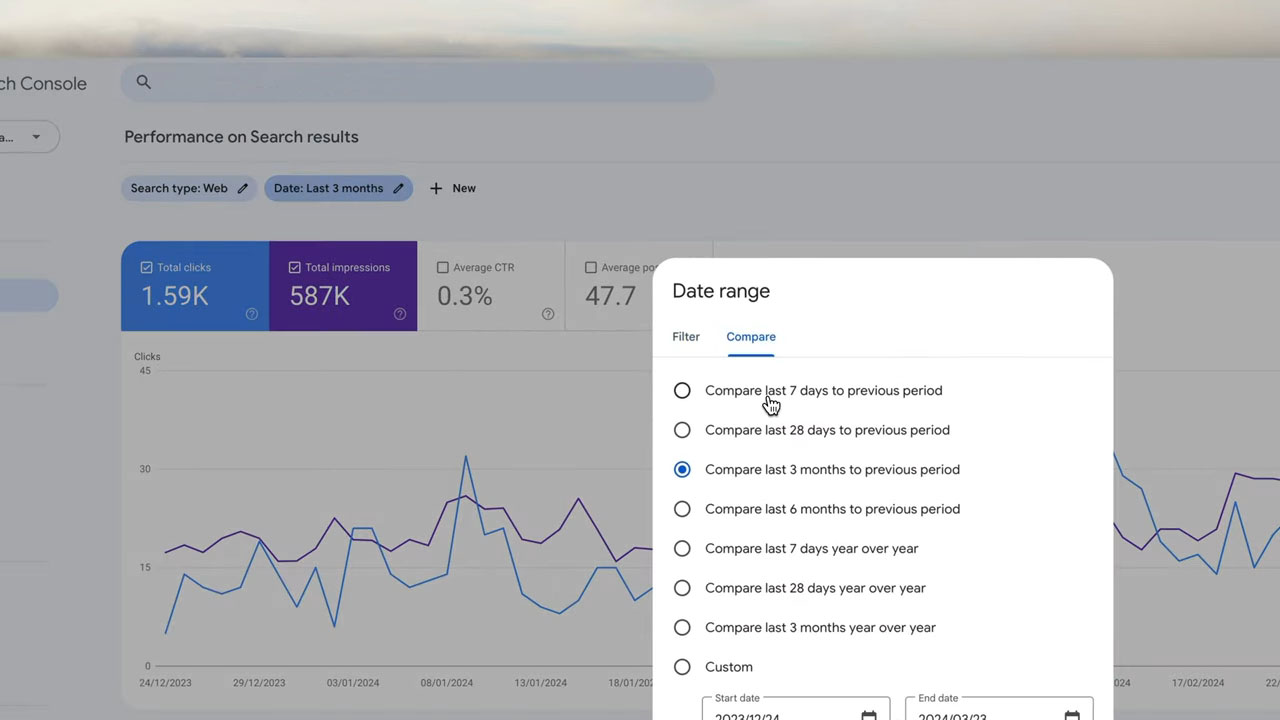
Before making any drastic cuts to your site, take time to evaluate what’s currently live. An effective audit sets the foundation for smart content pruning decisions and ensures you’re not removing content that still holds value in some way.
Start by gathering performance data. Use tools like Google Search Console, GSC Insights, Ahrefs, or similar platforms to review how each page is performing. Metrics alone won’t tell the full story, but they provide solid signals.
Content tied to your SEO strategy — especially those targeting organic search traffic — should be reviewed thoroughly. Not every page needs to top the rankings, but those meant to bring in visitors should at least justify their presence.
Key metrics to review:
| Metric | What It Indicates |
|---|---|
| Impressions | High impressions suggest Google recognizes the page’s relevance for certain queries. |
| Clicks | Low or declining clicks point to issues with visibility, relevance, or snippet attractiveness. |
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Strong CTR reflects engaging search snippets; weak CTR suggests users aren’t finding it worth clicking. |
| Keyword Rankings | Shows what keywords the page ranks for and how those positions have changed over time. |
| Backlinks | Quantity and quality of backlinks help determine SEO value; strong profiles may warrant retention. |
| Conversion Performance | Indicates lead generation, purchases, or signups — valuable even with low traffic. |
| Bounce Rate & Dwell Time | High bounce rate and low dwell time may suggest irrelevant or unengaging content. |
A page doesn’t need to excel in every area. Some may underperform in traffic but drive conversions or earn solid backlinks.
Others might rank well but see little engagement. Consider the full picture before deciding on the next step.
Step 2: Set Your Performance Benchmarks
Before deciding what to keep, improve, or remove, take a hard look at how each piece of content is actually performing. Not all underperformers are created equal.
Some pieces struggle due to keyword saturation, and others simply don’t convert. It’s not always black and white; that’s why establishing a clear set of performance metrics is critical.
Start by evaluating each page based on key signals. Use bullet points to track these indicators:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Impressions | Shows if your page appears in search and is understood by Google. |
| Keyword Presence | Checks if your page ranks for multiple related keywords. |
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Measures how often users click your page in search results. |
| Organic Clicks | Tracks how much qualified traffic your page receives. |
| Conversions | Shows if visitors take action like buying or subscribing. |
| Backlinks | Indicates if other websites link to your content. |
After reviewing each page with these metrics in mind, you’ll likely notice a pattern: some pages perform well in certain areas while lagging in others. That’s expected.
Not every metric will matter equally to every piece of content, but you should always ask: Is this page contributing something measurable?
Step 3: Choose the Right Action for Each Page
Don’t let low-performing pages just sit idle. Depending on the issue, there are different ways to revitalize or remove them:
Option 1: Update or Reoptimize
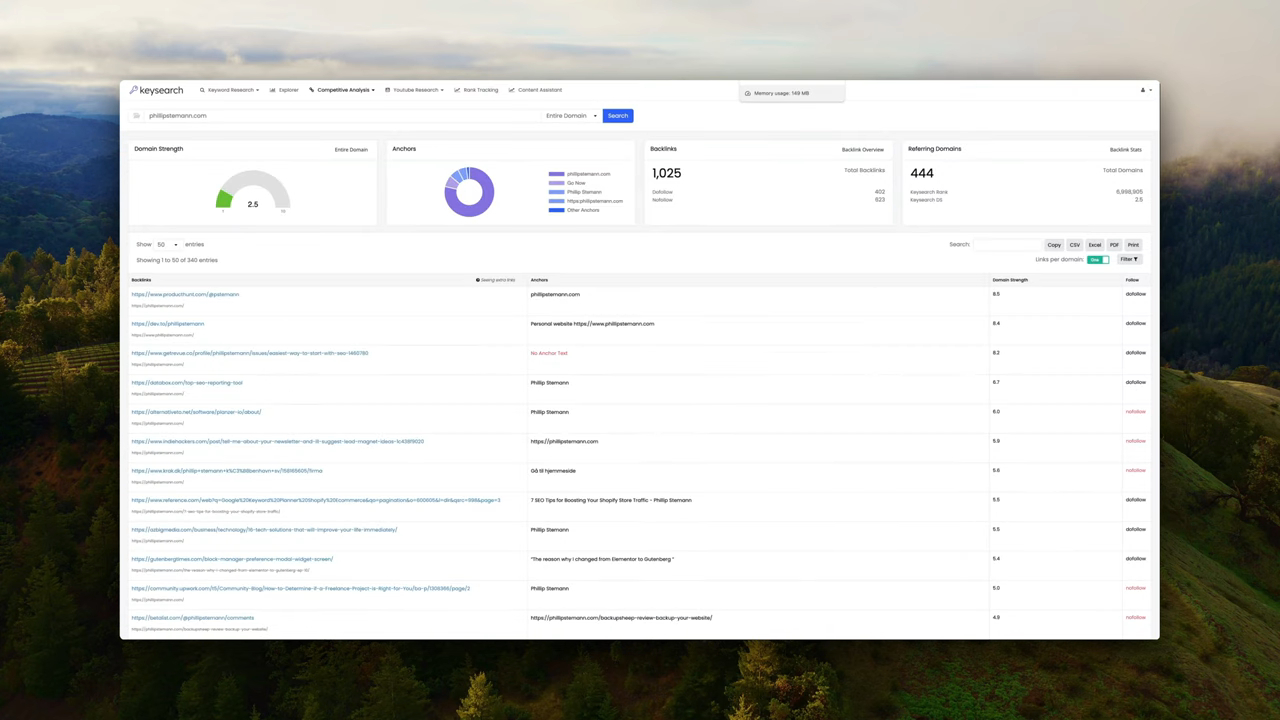
- When to consider: High impressions but low clicks.
If search engines are displaying your page frequently, but users aren’t clicking through, the issue likely lies in how the page presents itself in search results or the overall content quality.
It’s not enough to be seen—your page must give users a reason to engage. Improving visual and contextual signals can nudge users toward action.
- Refresh outdated elements – Update any old statistics, facts, broken links, or references to ensure information feels current and relevant.
- Increase topical depth – Add more substance to the content. Expand on existing sections or add new ones that address related questions users might have.
- Improve semantic relevance – Use SEO tools to fine-tune keyword usage. Tools that analyze top-performing search results can show you how to strengthen the topical focus of your content.
- Run A/B tests on key elements – Test different page titles, meta descriptions, and H1 tags to find what resonates more with your audience.
- Optimize for engagement – Add visuals, internal links, or clear calls to action that can help guide the reader through the page more effectively.
Top-performing content also deserves maintenance. Revisit those pages regularly to verify factual accuracy, link validity, and freshness. Even well-ranked content can slip if neglected.
Option 2: Realign or Retarget

- When to consider: High keyword competition or internal competition with similar pages.
At times, keyword landscapes evolve. What was once an easy keyword to target may now be overrun with heavyweight competitors.
Your content may also be suffering because it mirrors another page on your own site, leaving search engines confused about which one to prioritize.
- Choose a different keyword focus – Shift toward a more specific or lower-competition keyword that still fits the context of the page.
- Reposition the content angle – Adjust the content’s perspective or format to match different search intent or cater to a different audience segment.
- Launch a focused backlink strategy – Acquire high-quality backlinks to improve the content’s authority and help it better compete in search results.
Cannibalization between pages can dilute ranking potential. By differentiating page goals or consolidating keyword focus, you guide search engines toward promoting the right asset.
Option 3: Consolidate or Redirect
- When to consider: Existing backlinks or conversions but declining rankings.
Some content continues to provide value even after its traffic has slowed. If a piece still holds valuable backlinks or generates conversions, don’t rush to delete it. Reclaim that value by blending it with stronger assets or redirecting it to more relevant destinations.
- Use 301 redirects strategically – Redirect users and search engines to a page that offers higher quality or stronger conversions.
- Combine weaker pages into a comprehensive resource – If multiple light pieces of content cover similar themes, merge them into one detailed and informative page.
- Limit redirect chains – Keep things efficient. Avoid redirecting to a page that itself redirects elsewhere. Too many hops can reduce crawl efficiency and slow down load speeds.
Consolidation preserves equity while setting up your site for better future gains.
Option 4: Unpublish or Delete
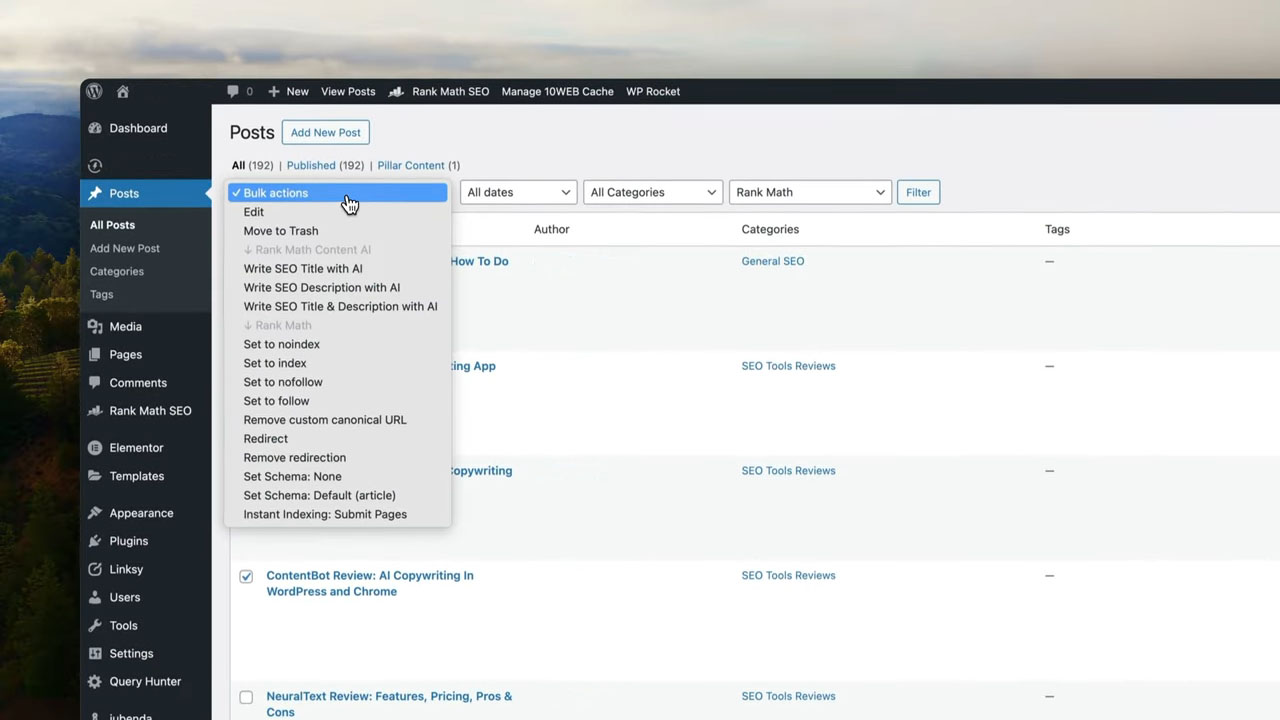
- When to consider: No impressions, clicks, backlinks, or identifiable value.
Not every piece of content deserves a second chance. If a page shows no signs of usefulness—no traffic, no visibility, no authority—it’s probably time to remove it.
- Start with content that clearly brings no benefit – Prioritize removal of the weakest pages first. These are pages that have no traffic history, generate no backlinks, and serve no strategic purpose.
- Wait and observe – Before mass deleting, give updated or redirected pages a few weeks. Track how those changes affect performance.
- Delete with care – Don’t remove large batches of content at once. Instead, be surgical and deliberate. Deleting too much too fast may confuse search engines or cause ranking shifts.
Sometimes, less truly is more. A leaner site with fewer distractions can help your best pages shine.
Signs That It’s Time to Prune
SEO operates in a shifting environment where nothing stays still for long. Content that once brought in traffic may now be stale, outdated, or simply outperformed by stronger pages—on your own site or elsewhere.
Search engine algorithms evolve, keyword competitiveness fluctuates, and user intent shifts.
If your site pushes out content regularly, it’s only a matter of time before certain pages fall behind. Content pruning helps determine which pages deserve a second chance and which ones have passed their expiration date.
| Sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Stagnant Traffic | Pages that have seen little to no organic growth over several months might no longer align with current search trends. |
| Zero or Minimal Impressions | When Google isn’t even showing your page to users, it suggests a lack of keyword relevance or crawl visibility. |
| Outdated Information | If data, visuals, links, or references haven’t been touched in years, chances are the content is no longer serving your users. |
| Thin Content | Pages with very low word counts and no clear value are rarely prioritized by search engines. |
| Duplicate or Overlapping Topics | Multiple pieces targeting the same keyword can cause internal competition and lead to ranking confusion—often referred to as keyword cannibalization. |
| High Bounce Rates with Low Engagement | If users visit a page and quickly leave without engaging, it’s a red flag about content quality or relevance. |
| Broken or Outbound Links Leading to Dead Pages | Outdated links within a post not only damage user trust but also send negative quality signals to search engines. |
| No Conversions or Internal Navigation Value | Content that fails to direct users toward a goal—newsletter sign-up, purchase, contact form, or even another page—isn’t helping your funnel. |
Pay attention to these warning signs, which indicate content pruning is absolutely necessary, because ignoring them can weaken site authority and slow down SEO momentum.
Final Thoughts
Content pruning is about working smarter, not harder. A well-maintained content library will serve your users better and send stronger signals to search engines.
Take time to analyze, adjust, and optimize — and your site will reward you with better rankings and more meaningful traffic.

